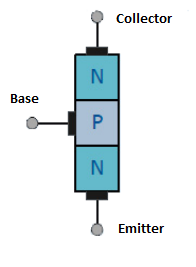
NPN transistor is a semiconductor device used as a switch or amplifier of electrical signals. It has a structure opposite to that of a PNP transistor.
In an NPN transistor:
- Charge carriers are electrons.
- Current flows from the collector to the emitter.
It consists of three semiconductor layers – one N-type (negatively charged) layer located between two P-type (positively charged) layers.
To open and activate an N-P-N transistor, you need to apply a “+” (forward current) to its base.
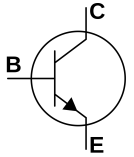
The fundamental principle of operation of any bipolar transistor is to control the base current to regulate the current flowing between the emitter and the collector.
When you apply voltage to the base of an NPN transistor, it causes current to flow through the base, which then controls the current between the emitter and the collector. When the transistor is turned on, current flows from the emitter to the collector. When the transistor is turned off, current cannot flow from the emitter to the collector.
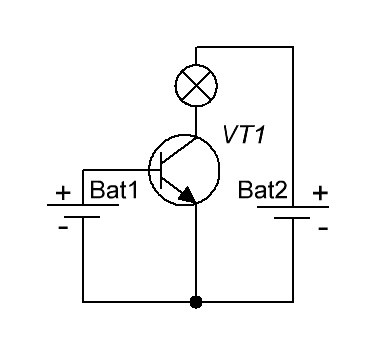
Transistors are used in various fields of application, such as in output stages of amplifiers, power supplies, electronic switches, and more.