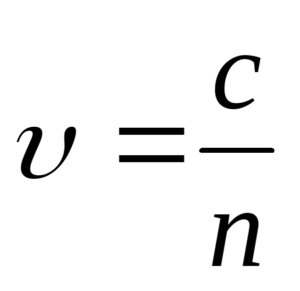Interference of light
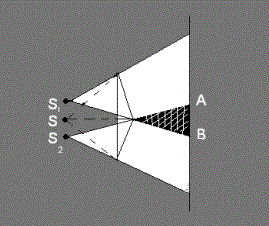
Interference of light is a physical phenomenon that occurs when two or more light waves intersect or overlap with each other. In the interference of light, both constructive and destructive wave interactions can be observed, leading to various phenomena such as light bands, color variations, or spots on surfaces. To obtain a stable interference pattern, …