A diode bridge, or a bridge rectifier, is an electronic device used to convert (rectify) alternating current (AC) to pulsating direct current (DC). It is composed of four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration.
An important part of electronic devices that are powered by the household electrical network with a voltage of 220 V and a frequency of 50 (60) Hz. As it is known, most devices require not AC but DC for their operation. Therefore, there is a need for rectifying AC current.
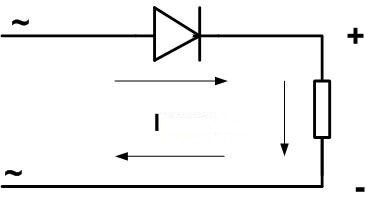
The purpose of a diode rectifier is to allow electric current to pass in one direction and prevent its reverse flow. The principle of its operation is based on the one-way conductivity – the property of a semiconductor diode to allow current to pass in only one direction.
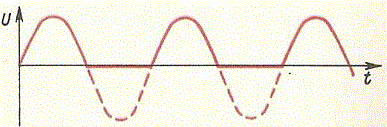
In this case, the diode will only allow the positive voltage (top part of the sine wave) to pass through, while it will “cut off” the negative voltage.
For full-wave rectification, a diode bridge is used.
The principle of operation of a diode bridge is as follows:
For example, in a power supply unit, a diode bridge is used as a rectifier. In circuits used in single-phase voltage networks, a diode bridge consists of four diodes.
AC voltage is applied to the input of the diode bridge, the polarity of which changes at a frequency of 50 Hz in household electrical networks.
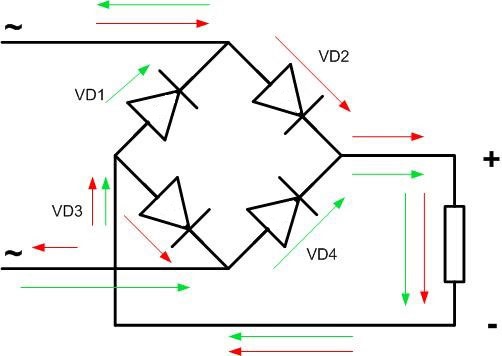
When there is a positive voltage (top part of the sine wave, indicated by a red arrow), the current will flow through diode VD2, the load, and VD3.
In case of negative voltage (lower part of the sine wave, green arrow), the current will flow through diode VD4, the load, and VD1.

As a result, during each period, the current passes twice through the load in the same direction.
Diod bridges (single-package)
Bridges can be assembled from individual discrete diodes and can be made in the form of a single-package device (diode assemblies).

Single-package implementation is preferred for regular applications as they are cheaper and smaller in size. The diodes in such a package are selected by the manufacturer and have similar maximum allowable parameters.
One disadvantage of a single-package implementation is that if one of the diodes fails, the entire component needs to be replaced. In bridges made of discrete diodes, only the failed diode needs to be replaced.