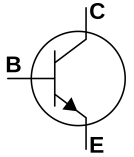
PNP transistor

PNP transistor is a semiconductor device with a structure opposite to that of an NPN transistor. It has an N-type layer situated between two P-type layers. In a PNP transistor: When you apply current to the base of a PNP transistor, which controls the current between the emitter and the collector, the transistor turns on. …