Diode

ЗмістThe principle of operation of the diodeForward biasing of a diode (p-n junction)Reverse biasing of a diode (p-n junction)Volt-Ampere characteristics of a diode (p—n – transition).Diode packages Diode is a two-terminal electronic component that has different electrical conductivity depending on the polarity of the applied voltage. Diodes can be vacuum (rectifiers), gas-filled (gas diodes, ignitrons, …
1n4003 datasheet
data sheet 1n4002
1n4001 data sheet
Electroscope
Electromagnet

An electromagnet is a coil with a ferromagnetic core inserted into it. The magnetic field of a current-carrying coil is of particular practical interest. If a coil with current is suspended on thin and flexible wires, it will align itself just like a compass needle: one end will point north, and the other end will …
Dispersion of light

Dispersion of light (light breakdown; light scattering) is the phenomenon of breaking down light into a spectrum due to the dependence of the refractive index of a medium on the frequency of the light wave. light scattering is the phenomenon of breaking down white light into its component colors. The reason for this breakdown is …
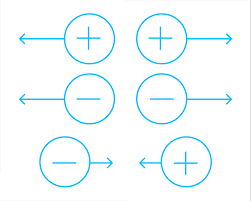
Electric charge
Titanium

Titanium (chemical symbol – Ti, from Latin Titanium) is a chemical element of the 14th group (formerly classified as a subgroup of the fourth group, IVB) of the fourth period of the periodic table of chemical elements by D. I. Mendeleev, with an atomic number of 22. Group of metals: Refractory lightweight metal Atomic number: …